What is Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio?
May 18, 2025The price-to-earnings ratio is a company’s share price divided by its earnings per share. The resulting number is shown as a multiple and represents how much an investor is paying for each $1 in profit a company generates. If a company’s P/E is 10.2x, then an investor in the company’s stock is paying $10.20 per $1 of earnings. Investors often use the P/E ratio to quickly and easily compare the valuations of different companies, or as a benchmark to value a standalone company.
What is a Good P/E Ratio?
A good P/E ratio can vary from investor, though many agree that companies with a ratio lower than 15.0x to be a value stock, while companies with ratios above 15.0x may be considered growth stocks. However, different types of companies typically have different average P/E ratios. For example, as of January 2025, the Software (Internet) industry has a P/E of 51.76x, while the Rubber & Tire industry has a P/E of 7.38x. Investors are willing to pay ~$52 per $1 of Software earnings, but just ~$7 for the same $1 that a Tire company generates.
Why Does P/E Vary by Industry?
P/E varies by industry for many reasons, with the most common being growth prospects. If two companies earn the same profits, but Company A is projected to grow twice as fast as Company B, then investors may be willing to pay twice as much for Company A’s stock on a P/E basis compared to Company B. This example shows that P/E is a point in time metric, and is calculated based on historical earnings. For this reason, investors must assess P/E in context of historical and forward-looking information.
Limitations of P/E Ratio
There are multiple drawbacks of the P/E ratio, though the most impactful is that the P/E ratio is a point in time metric and only captures today’s price and earnings over a 12 month period. Daily fluctuations in a stocks price can change the P/E ratio although the underlying earnings of the business have not changed. Alternatively, one good or bad period of earnings over the last 12 months may shift the P/E ratio in a way that does not reflect the long-term performance of the company. Therefore, investors must pair their assessment of a company’s P/E ratio alongside other valuation methods.
How to Calculate P/E Ratio
The P/E Ratio is calculated as a company’s share price divided by its earnings per share:
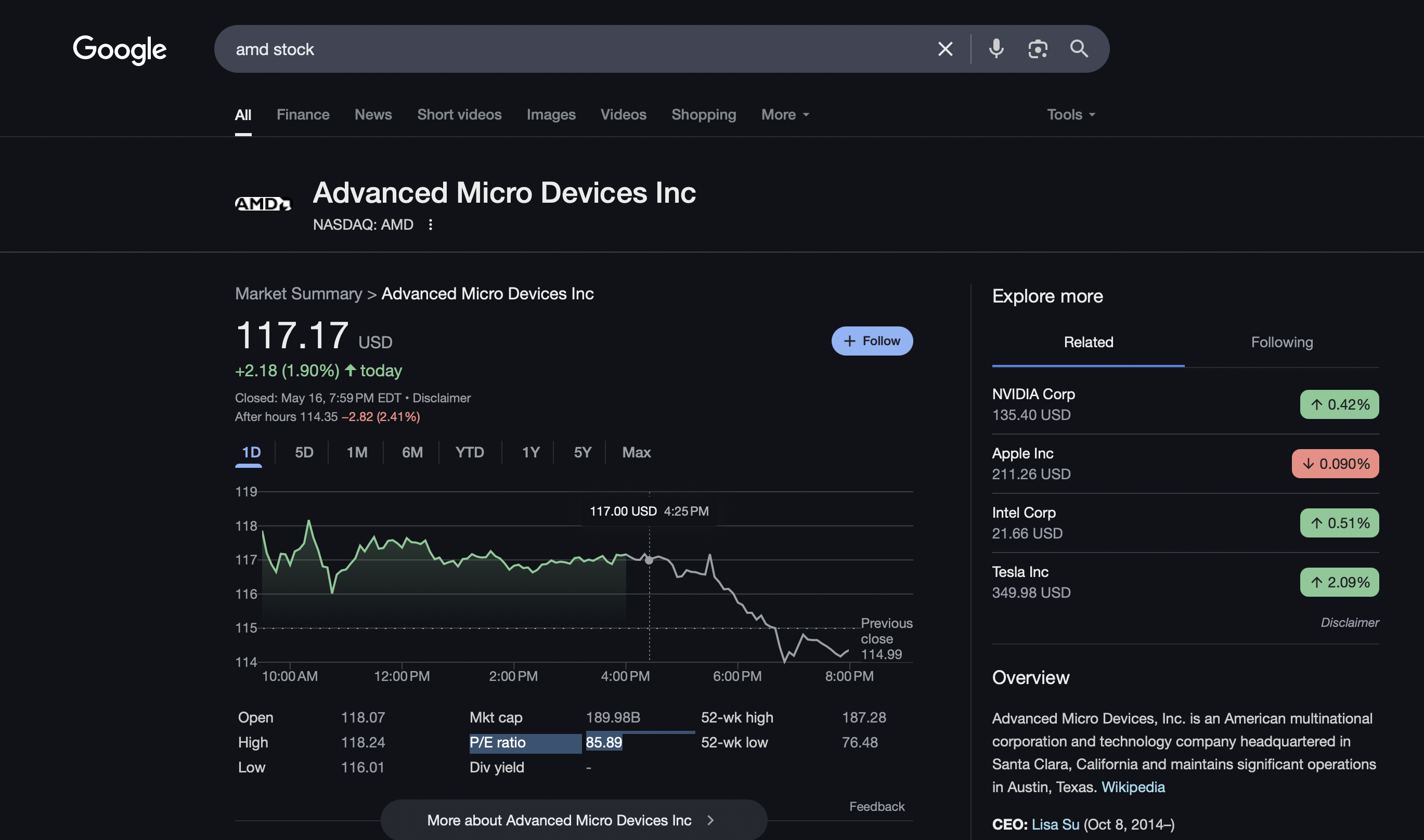
A company’s P/E ratio can readily be found via Google search, eliminating the need to calculate P/E manually. For example, AMD’s P/E is 85.89x as shown in the bottom of the below screenshot.